Workflow means performing any task in order. Today, each application is based on workflow approach
and involves some processes to be executed. While creating an application, developers are still following
the traditional approach that leads to create steps in the process implicit in the code. This traditional
approach works fine, but requires a deep programming logic making the process difficult to change and execute.
Workflow engine is not a new technology; it came into existence in early 2000. In the market, several
workflow engines are available for Windows and other platforms. Today, all applications are based on
workflow approach. So, defining different engines for different applications is a cumbersome task. To
avoid this, Microsoft has decided to define a single common workflow engine for all the windows-based
applications. This is what the Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) performs. WF provides a common
workflow technology for all the windows-based applications, such as Microsoft Office 2007 and
Windows Share Point Services.
ASP.NET is a development framework for building web pages and web sites with HTML, CSS, JavaScript and server scripting. ASP.NET supports three different development models: Web Pages, MVC (Model View Controller), and Web Forms.
Tuesday, February 26, 2008
Data loading from SQL Server database at runtime
Firstly Add DataList Control in Design View.Then Change the html code of Datalist as follows:

Source Code:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Collections;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public partial class dynamic : System.Web.UI.Page
{
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection("Data Source=ELWIN;Initial Catalog=sherin;Integrated Security=True");
public void display(string query)
{
con.Open();
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter(query, con);
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
da.Fill(dt);
DataView dv = new DataView(dt);
PagedDataSource objpag = new PagedDataSource();
objpag.DataSource = dv;
objpag.AllowPaging = true;
objpag.PageSize = 5;
DataList1.DataSource = objpag;
DataList1.DataBind();
con.Close();
}
public void check(object sender, System.Web.UI.WebControls.CommandEventArgs e)
{
if (Session["programid"] != null)
{
Session["programid"] = Session["programid"] + " or programid=" + e.CommandName;
}
else
{
Session["programid"] = e.CommandName;
}
string fg = Session["programid"].ToString();
Response.Redirect("shoppingcart.aspx");
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Page.IsPostBack)
{
display("select * from addprogram2 ");
}
}
}
Output:


Source Code:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Collections;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public partial class dynamic : System.Web.UI.Page
{
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection("Data Source=ELWIN;Initial Catalog=sherin;Integrated Security=True");
public void display(string query)
{
con.Open();
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter(query, con);
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
da.Fill(dt);
DataView dv = new DataView(dt);
PagedDataSource objpag = new PagedDataSource();
objpag.DataSource = dv;
objpag.AllowPaging = true;
objpag.PageSize = 5;
DataList1.DataSource = objpag;
DataList1.DataBind();
con.Close();
}
public void check(object sender, System.Web.UI.WebControls.CommandEventArgs e)
{
if (Session["programid"] != null)
{
Session["programid"] = Session["programid"] + " or programid=" + e.CommandName;
}
else
{
Session["programid"] = e.CommandName;
}
string fg = Session["programid"].ToString();
Response.Redirect("shoppingcart.aspx");
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Page.IsPostBack)
{
display("select * from addprogram2 ");
}
}
}
Output:

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
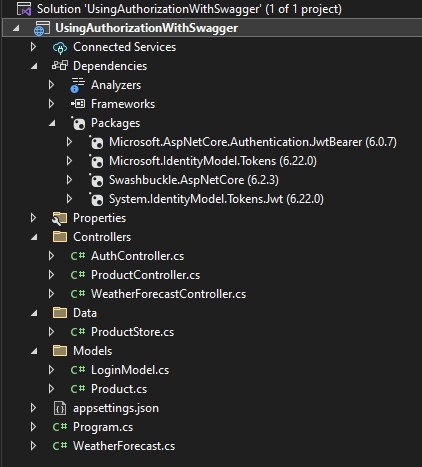
Using Authorization with Swagger in ASP.NET Core
Create Solution like below LoginModel.cs using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; namespace UsingAuthorizationWithSwagger.Models { ...
-
Codebehind C#: public static Bitmap CreateFirstCard(string Name,string MembNo,string Mobile,string Phone, ...
-
VideoGallery.aspx <div class="matter-area fl"> <h2>Videos</h2> <p> <asp:Repeater ID=...
-
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.D...


